In the realm of lifestyle medicine, understanding the differences between movement, physical activity, and exercise is crucial for promoting health and well-being. Each of these components plays a unique role in maintaining optimal health, and incorporating them into daily life can lead to significant improvements in overall fitness and quality of life.
Movement vs. Physical Activity vs. Exercise
Movement
Movement refers to any change in the position of the body. It is the most basic form of physical engagement and is essential for everyday functioning.
Physical Activity
Physical activity encompasses any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure. This includes a wide range of activities, from walking and cycling to gardening and household chores.
Exercise
Exercise is a structured form of physical activity with the specific goal of improving and maintaining health and physical fitness. It is deliberate and often involves planned, repetitive movements to enhance strength, endurance, and flexibility.
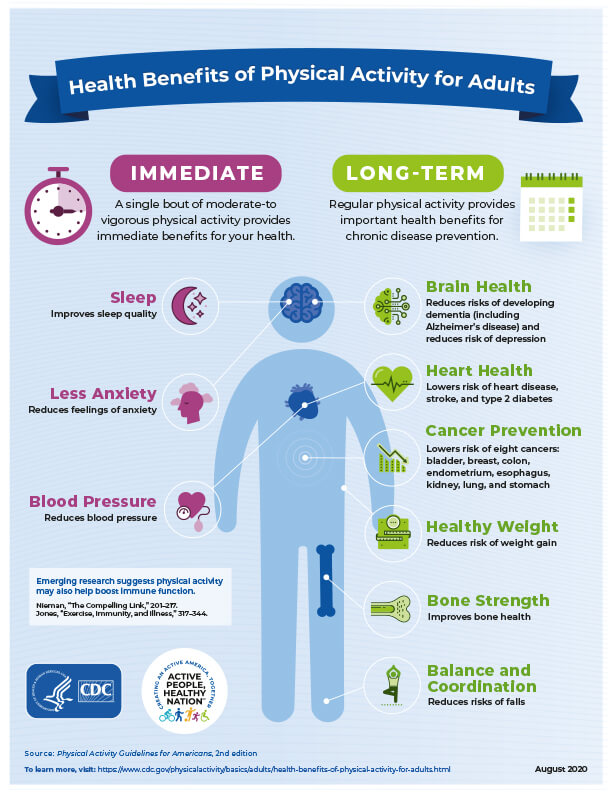
Key Components of Physical Activity
1. Aerobic/Endurance Exercise
Aerobic exercise, also known as cardiovascular or endurance exercise, involves rhythmic movements of large muscle groups over an extended period. This type of exercise is pivotal in improving cardiovascular fitness and offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reducing the risk of all-cause mortality
- Lowering the incidence of cardiovascular diseases and various types of cancers
- Enhancing overall quality of life and sleep
2. Strength/Resistance Exercise
Strength or resistance exercise involves contracting muscles against an external resistance to increase lean body mass and enhance muscular strength and endurance. The benefits are extensive:
- Reduces injury risk
- Boosts basal metabolic rate (BMR)
- Alleviates fatigue and promotes better sleep
- Enhances overall physical performance and muscle strength
- Improves bone mineral density and reduces body fat
- Supports weight management and enhances body aesthetics
- Improves cholesterol levels and glucose control
- Decreases pain and disability associated with arthritis
- Reduces the risk of falls in the elderly and enhances mental health
3. Flexibility Exercises
Flexibility exercises focus on the range of motion achievable at joints and are influenced by factors such as muscle and tendon tightness. Activities like stretching, yoga, Tai Chi, and Pilates are excellent examples. Benefits include:
- Increasing muscle length and range of motion
- Aligning collagen fibers and aiding muscle healing
- Improving gait by increasing stride length and peak hip extension
- Contributing to recovery, soreness prevention, injury prevention, and performance enhancement
4. Neuromotor Activities and Balance Training
Neuromotor activities and balance training are crucial for maintaining equilibrium while stationary or in motion. These activities enhance the ability to withstand postural sway and destabilizing stimuli, such as walking backward or standing on one leg. The benefits are significant:
- Reduces fall-related injuries, including a decrease in overall falls, injuries requiring medical care, severe injury falls, and falls resulting in fractures
Conclusion
Incorporating these components of physical activity into daily life is essential for achieving and maintaining optimal health. Whether through structured exercise routines or simple daily movements, staying active is key to a healthier, more fulfilling lifestyle. Embrace the power of movement, physical activity, and exercise to transform your health and well-being.
Stay active, stay healthy!
